PET Plastics | An Introduction
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) plastic is a versatile and widely used polymer that has become an integral part of our daily lives. It is a thermoplastic material that is formed through the polymerization of ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. PET plastic is known for its strong, lightweight, transparent, and durable properties, making it suitable for various applications. Let’s delve deeper into the world of PET plastic to understand its uses, recyclability, history, frequently asked questions, safety aspects, and what the future holds.

PET Uses
PET plastic finds extensive use in a wide range of industries due to its exceptional properties. One of its primary applications is in the packaging industry, where PET bottles and containers are manufactured. These bottles are commonly used for beverages, such as water, soft drinks, juices, and sports drinks. The clarity of PET plastic allows consumers to easily visualize the contents, while its lightweight nature makes it convenient for transportation.
Furthermore, PET plastic is also utilized in the textile industry to produce fibers, known as polyester. These polyester fibers are commonly used in clothing, carpets, upholstery, and other textiles. PET films, sheets, and trays are employed in the production of packaging materials, thermoformed products, and electrical insulation. In recent years, PET has even found its way into 3D printing, enabling the creation of intricate and durable objects.
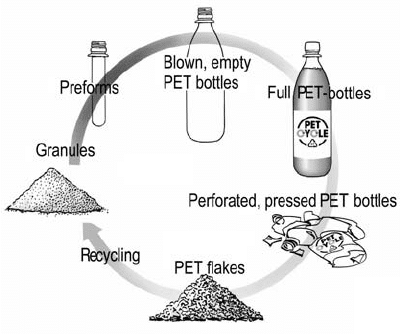
Is PET Plastic Recyclable?
Yes, PET plastic is highly recyclable and is one of the most recycled types of plastic worldwide. The recycling process for PET involves several stages, starting with collection and sorting of the plastic waste. Once sorted, the PET plastic is cleaned, ground into small flakes, and then melted to form new raw material. This recycled PET, commonly referred to as rPET, can be used to produce a wide range of products, including new bottles, fibers, sheets, and packaging materials.

The recycling of PET plastic offers numerous environmental benefits. It helps reduce the demand for virgin plastic resin, conserves energy, lowers greenhouse gas emissions, and mitigates the impact of plastic waste on landfills and marine ecosystems. Additionally, recycling PET promotes a circular economy by closing the loop and giving plastic a second life.
To ensure effective PET plastic recycling, it is crucial for consumers to properly dispose of their PET waste in designated recycling bins. Governments, organizations, and individuals should also support initiatives that promote the development of recycling infrastructure and the use of recycled PET in various industries.
A Brief History of PET Plastic
The history of PET plastic dates back to the mid-20th century when two British chemists, John Rex Whinfield and James Tennant Dickson, invented the material in 1941. Initially, PET was primarily used as a textile fiber, but its potential as a packaging material became evident in the 1970s. The Coca-Cola Company played a significant role in popularizing PET bottle packaging, introducing the first PET bottle for beverages in 1977.
Since then, PET plastic has gained immense popularity due to its unique combination of properties, replacing traditional packaging materials such as glass and aluminum in many applications. The advancements in PET manufacturing technology have enabled the production of lightweight, shatter-resistant, and easily recyclable bottles, revolutionizing the beverage industry.
In recent years, efforts have been made to further enhance the sustainability aspect of PET plastic. This includes the development of plant-based or bio-based PET, which utilizes renewable resources instead of fossil fuels in its production. These innovations aim to reduce the environmental impact of PET production and expand its range of applications.
The Science and Creation of PET
PET plastic is synthesized through the polymerization of two main monomers: ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. The process involves several steps, starting with the production of the monomers themselves.
Ethylene glycol, also knownas ethane-1,2-diol, is derived from ethylene oxide. Ethylene oxide is first produced by the oxidation of ethylene gas in the presence of a catalyst. This ethylene oxide is then hydrolyzed to produce ethylene glycol.
Terephthalic acid, on the other hand, is typically produced through a two-step process. The first step involves the oxidation of para-xylene, a hydrocarbon derived from petroleum, to form crude terephthalic acid. The crude terephthalic acid is then purified through processes such as crystallization or solvent extraction to obtain high-quality terephthalic acid.
Once the ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid are obtained, they are combined in a reactor under specific conditions of temperature and pressure. The reaction between the two monomers results in the formation of PET polymer chains through a process called condensation polymerization. During this process, water is released as a byproduct.
The PET polymer chains formed can vary in length, which affects the properties of the resulting plastic. Typically, longer chains create a higher molecular weight PET, which is more rigid and has a higher melting point. Shorter chains, on the other hand, result in lower molecular weight PET, which is more flexible and easier to process.
After the PET is synthesized, it can be further processed into various forms, such as pellets, sheets, or fibers, depending on the intended application. These forms can then be used for manufacturing PET bottles, textiles, films, and other products.
The FAQs of PET Plastic
Is PET Plastic Safe?
PET plastic is generally considered safe for use in various applications, including food and beverage packaging. It has been approved by regulatory authorities such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) for contact with consumable products.
PET is inert and does not react with food or beverages, ensuring that there is no transfer of harmful substances from the packaging to the contents. It also provides a strong barrier against oxygen, carbon dioxide, and moisture, which helps preserve the quality and freshness of the packaged products.
However, it is important to note that PET should be used within its intended temperature limits. Excessive heat can cause PET to soften, potentially leading to leaching of chemicals. Therefore, it is best to avoid using PET containers for hot liquids or microwaving them unless specifically labeled as microwave-safe.
What does PET plastic mean?
PET stands for Polyethylene Terephthalate, which refers to the chemical composition of the plastic. It is a polyester polymer made from the monomers ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. PET plastic is known for its clarity, strength, and versatility, making it suitable for various applications, particularly in packaging and textiles.
Is PET plastic BPA-free?
Yes, PET plastic is free of Bisphenol A (BPA). BPA is a chemical compound that has been used in the production of some plastics, but it has raised concerns due to its potential health effects. However, PET does not contain BPA, and it is considered a safer alternative in terms of chemical leaching.
PET has its own resin identification code, which is number 1 inside the recycling symbol. This code helps with the identification and sorting of different types of plastics for recycling purposes.
The Future of PET

The future of PET plastic looks promising, driven by ongoing efforts to improve its sustainability and expand its applications. Here are some developments and trends that can shape the future of PET:
- Bio-based PET: Researchers and companies are exploring the use of bio-based or plant-based sources for PET production. By utilizing renewable resources, such as sugarcane or corn, instead of fossil fuels, the environmental impact of PET manufacturing can be significantly reduced. Bio-based PET has the potential to become a more sustainable alternative while maintaining similar properties to conventional PET.
- Recycling advancements: Initiatives are focused on improving PET recycling processes and infrastructure. Advanced technologies, such as enhanced sorting methods and depolymerization techniques, aim to increase theefficiency of PET recycling and promote the use of recycled PET (rPET) in various industries. These advancements can help reduce the reliance on virgin plastic and contribute to a more circular economy.
- Innovation in applications: The versatility of PET plastic opens up opportunities for innovative applications. Companies are exploring new uses of PET beyond traditional packaging and textiles. For example, research is being conducted on utilizing PET in the development of sustainable building materials, automotive components, and medical devices. These innovations can further expand the market for PET and increase its value as a recyclable material.
- Increased consumer awareness: The growing global awareness about plastic pollution and sustainability has resulted in increased consumer demand for environmentally friendly products. This shift in consumer behavior encourages businesses to adopt sustainable practices, including the use of recyclable and eco-friendly materials like PET. As consumers continue to prioritize sustainability, the demand for PET alternatives and recycled PET products is expected to rise.
- Regulatory measures: Governments and regulatory bodies are implementing policies and regulations to address plastic waste and promote sustainable practices. These measures include plastic bans, extended producer responsibility programs, and incentives for using recycled materials. Such regulations can shape the future of PET by incentivizing its recycling and encouraging the adoption of more sustainable alternatives.
In summary, the future of PET plastic is marked by advancements in sustainability, recycling technologies, innovative applications, increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly products, and supportive regulatory measures.
Conclusion
PET plastic, or Polyethylene Terephthalate, is a versatile and widely used material that has transformed various industries, particularly packaging and textiles. Its exceptional properties, recyclability, and safety make it a preferred choice for many applications. Understanding the science behind PET production, its history, and its potential future developments helps us appreciate its significance in our lives. With ongoing efforts towards sustainability and innovation, PET plastic continues to evolve and adapt to meet the changing needs of a more environmentally conscious world.

